December 2, 2024
December 2, 2024  10 min to read
10 min to read It is crucial for today’s warehouses, which are adjacent to a manufacturing facility, to meet customer expectations regarding high product quality and efficient distribution. If a company is considering potential cost-reduction strategies, a WMS is the most appropriate solution and can affect all operating expenses in the long term. Since many companies today look at warehousing costs as a percentage of sales or production costs, a WMS is a way to reduce overall warehousing and production costs. We have outlined a key framework on how to overcome bidding hurdles when contracting WMS software, which can minimize uncertainty among manufacturing and warehousing companies.
WMS implementation costs
Companies looking to implement a WMS must consider several elements and involve costs essential for a successful project launch.
- Audit fees – are required to prepare an entire business needs assessment to estimate the scope of further implementation. In many cases, companies that do not have in-house resources can use third-party consulting companies for WMS scope evaluation, which generates potential costs at the beginning of the implementation process. In some exceptions, third-party software companies can offer free on-site installed demos with consultancy; manufacturing companies can test software solutions before implementation.
- Information technology costs – WMS software can include several licenses as cost-per-user, which is a very affordable solution because the company can keep up with sustained growth and increase the supply of user licenses with increased operational demand. The IT costs include integration costs per system user and connector solutions for ERP systems, printer software, IoT connectors to manufacturing machines and robots, etc. Other costs are related to the environment, including development, testing phase, and production as user integration solutions. Nowadays, WMS software is offered in the SaaS model; therefore, companies must cover hosting Cloud costs or On-Premise maintenance, but these costs may instantly cover customer service support.
- Hardware costs – handheld barcode scanners are essential for seamless WMS operations, allowing employees to work remotely with other useful functions. This is the necessary equipment needed for any WMS to perform optimally. Final equipment needs are determined by internal requirements and can vary, but instead of purchasing equipment directly, a manufacturing company can use equipment leasing/rental, which provides a temporary business depreciation and lowers implementation costs.
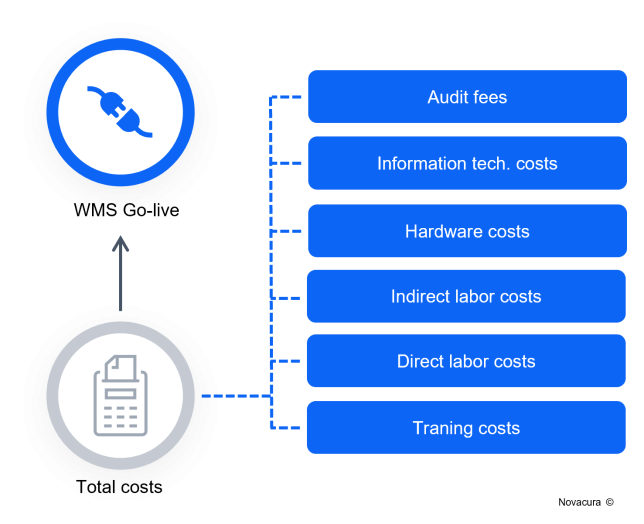
- Indirect labor costs – supervision of the project by in-house personnel such as administrators, quality controllers, and procurement staff, including hours worked and wages with additional fees, which are assigned to the project by the company. These costs arise from collaboration between internal teams and third-party personnel from software vendors.
- Direct labor costs – on-site implementation of the project with support from a third-party software provider, including working hours booked for business consulting and support software developers. Labor hours relate to the development of the system environment, testing phases, and time required for the final production environment.
- Training costs – personnel training costs are generated while WMS is ready to Go-Live phase. In this case, the process is connected to overhanging manuals and explanation functionalities to operations staff. WMS software should provide maximum flexibility and easy to follow interface for mobile applications for hand scanners to decrease training time and involved costs.
WMS implementation scope
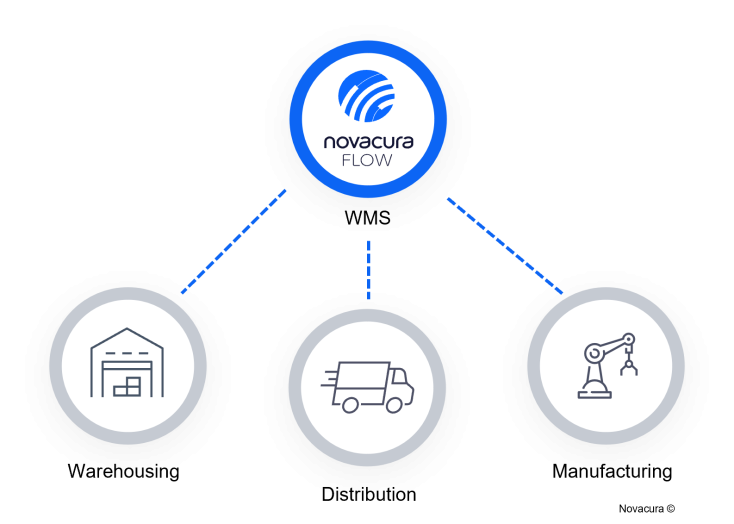
Lean techniques, as well as substantial audits conducted by third-party software providers, allow companies to evaluate internal requirements and scope for WMS implementation. Complete WMS software must provide sustainability in warehousing, distribution, and manufacturing to be most efficient by establishing a connection between all systems and operations.
Warehousing
Depending on inventory characteristics and production requirements, it is important to consider asset storage needs and other operational requirements for order picking, the flow of supplies between storage and the shop floor, the number of software users, etc. In some exceptions, well-functioning WMS might be the solution to eliminate outside storage facilities and consolidate all operations with inventory into a manufacturing facility, at the same time reducing facility and operational costs.
Distribution
Internal goods distribution from shelves in the warehouse to the shop floor and ensuring raw material cycle, but also order picking and shipping with scraps management with returnable packaging material management, etc. WMS distribution scope covers supply chain demand that helps integrate delivery time to warehouse and customers. Implementation of WMS should include distribution evaluation as one of the key elements.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing operations on the shop floor, including robotics on a production line or machinery to components processing, may require the use of IoT connectors to keep data exchanged between WMS and ERP systems. In that way, shop floor operations provide constant data feed for the warehouse and supplies from inventory. The WMS for manufacturing should consider shop floor requirements, which helps arrange warehouse setup as spare parts storage, work-in-progress storage, etc.
How to implement a WMS
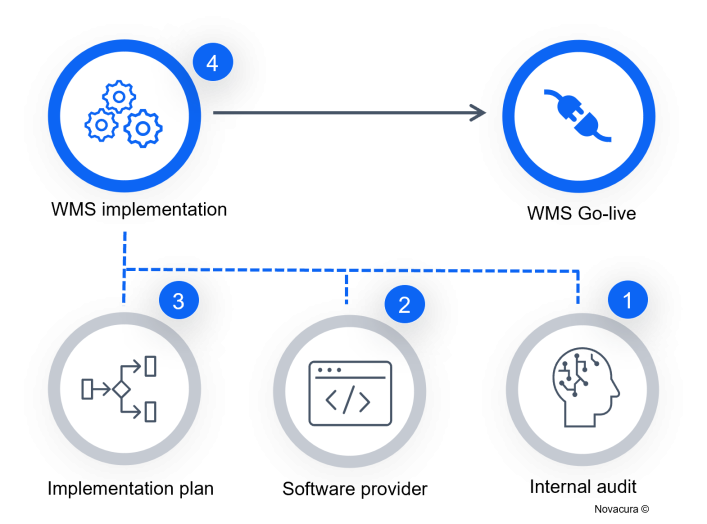
To implement a WMS, the company should determine which software will be most suitable for its manufacturing and warehouse operations. Only WMS vendors that have access to software technology independent of third-party solutions, as well as in-house BPM experience and manufacturing industry expertise, are the most appropriate choice to implement a WMS and provide ongoing support. Here are the key elements that correspond to the ultimate WMS implementation guideline:
- Conduct an internal audit – contact an auditing company or directly with a software vendor that can audit internal operational requirements for a WMS and provide you with a demo.
- Choose a software provider – companies with a proven track record and that can provide ongoing support before and after implementation are usually the best choice.
- Create an implementation plan – align internal resources with the WMS software vendor and plan the implementation steps with the scope of work.
- Implement the WMS – implement the WMS in stages to increase operability step by step, rather than to replace existing processes right away (in some cases, a company can implement a WMS immediately, but this requires a well-developed plan).
Novacura is a company that provides Novacura Flow software with WMS functionality that can be connected to ERP systems. Novacura Flow software can support manufacturing and warehousing operations by giving users access to a platform that enables business process design (BPM with Novacura) and the building of customized mobile and desktop applications to exchange data with ERP systems. The low-code platform-based solution gives users full operational flexibility to customize ERP transactions without costly modifications.
Media error: Format(s) not supported or source(s) not found
Download File: https://www.novacura.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/nc-www-app-creation-in-flow.mp4?_=1The example presented above explains how users can build own app with Novacura Flow, that gives its users access to Novacura Flow Studio, environment for developing applications for internal operational needs in manufacturing industry.
Warehouse Management System implementation
Novacura Flow integrated with existing warehouse and manufacturing architecture enables the following WMS functionalities:
- Deep ERP integration – the ERP system used on site and its existing transactions are fully integrated with the Novacura Flow low-code platform and mobile/desktop applications based on the low-code (read here more about Deep ERP integration).
Media error: Format(s) not supported or source(s) not found
Download File: https://www.novacura.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/deep-integrations-online-effects-in-erp-animation2.mp4?_=2- Interconnected systems – ensures connectivity and compatibility with all external and internal systems (compliance labeling, reporting systems, etc.), both those supporting internal operations and those external to suppliers/vendors/customers.
- IoT connectors – Novacura provides +50 connectors to help connect manufacturing equipment, sensors, barcode scanners, etc., to get instant data to WMS and ERP processes.
- Business customization – the low-code platform allows for continuous BPM customizations and mobile/desktop application development without harassing existing processes.
- Easy training – business applications are customized with an interface tailored to a company’s internal needs, so processes and transactions are designed to be easy to follow, reducing training time for new employees and allowing handling all changes internally.
- Low costs – the low-code platform helps keep fixed business costs low, as company personnel can make any operating software modifications easily.
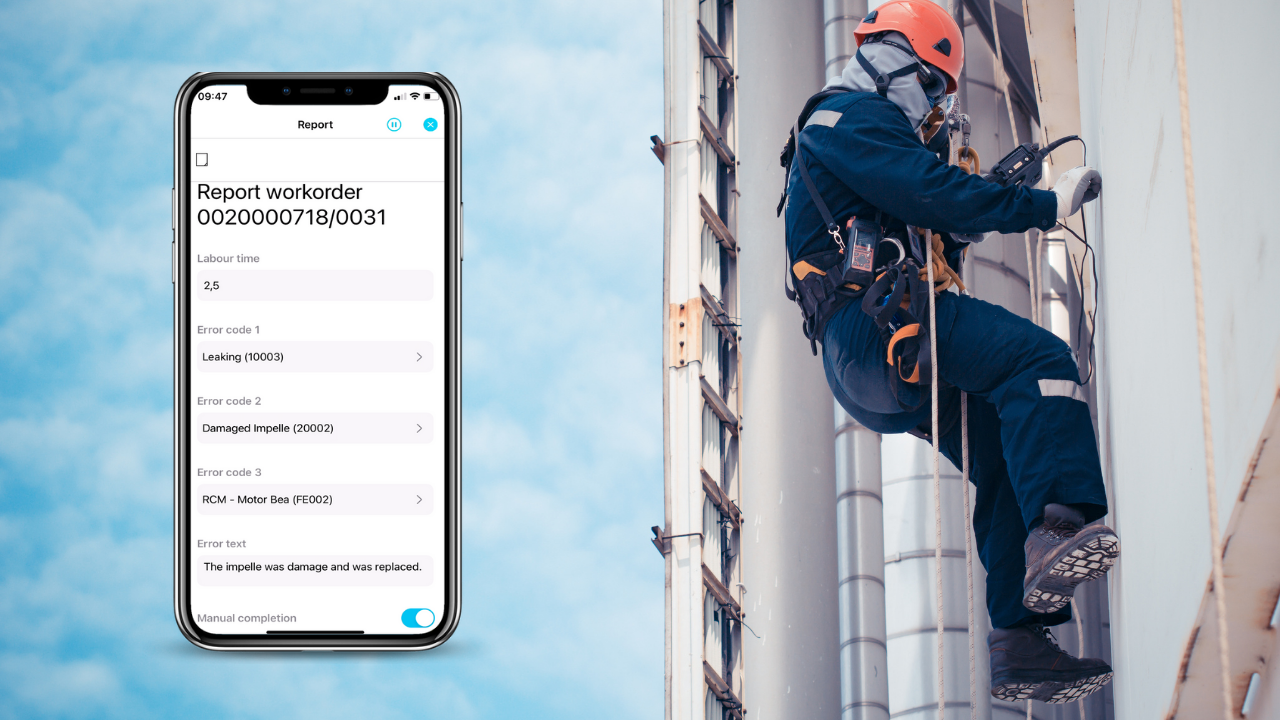
Media error: Format(s) not supported or source(s) not found
Download File: https://www.novacura.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/material-requistion-app-5.mp4?_=3Create Material Requisition Line mobile application from Novacura enables the efficient transfer of materials from the warehouse to the shop floor. Production line operators can easily order the required raw materials, parts, etc. needed for production and avoid delays.
Post-Implementation Support and Continuous Improvement
Successful WMS implementation doesn’t end at the Go-Live phase; ongoing support and continuous improvement are essential to maximize system efficiency and adaptability. Post-implementation support offers businesses a way to address any unforeseen challenges and optimize the WMS to meet changing operational demands.
1. Technical Support and Troubleshooting
Having access to dedicated technical support ensures that any system issues are promptly addressed, minimizing potential downtime. Reliable support teams can provide solutions for both minor troubleshooting needs and more complex adjustments, allowing the WMS to operate smoothly even as the company scales.
2. Regular Software Updates
WMS providers often roll out updates to enhance functionality, security, and performance. These updates help companies stay current with industry advancements and prevent vulnerabilities. A system that evolves with regular updates allows businesses to remain competitive without the need for extensive reimplementation.
3. Employee Training and Skills Development
As new features and updates are introduced, continuous training programs help keep employees up-to-date on system capabilities. Regular training not only empowers staff to use the WMS more effectively but also reduces the likelihood of errors and increases overall productivity.
4. Feedback Loops for Process Optimization
Continuous improvement involves gathering feedback from end-users to identify areas where the WMS can be optimized further. Creating feedback loops allows companies to make incremental improvements, aligning the WMS more closely with operational workflows and maximizing its utility over time.
5. Scalability and Customization
Effective post-implementation support includes the ability to scale and customize the system as business needs evolve. A flexible WMS that grows with the company can accommodate increased inventory, additional users, or new functionality, ensuring that the system continues to support the business effectively in the long term.
Continuous improvement and post-implementation support ensure that the WMS not only meets today’s needs but is also adaptable for future growth and changes, providing companies with long-term value and a sustainable competitive advantage.
Summary
Implementing a WMS should take lean principles into account, as its goal is to remove all activities that use resources but do not create additional value. In practice, this means that the WMS should be as flexible as possible to streamline current processes. This is one of the main features offered to manufacturing and warehousing companies, along with Novacura’s nearly 20 years of experience in software implementations.
Get app package Shop Floor Reporting
- The shop floor reporting app provides a variety of manufacturing-related reporting possibilities for shop floor users.
- Barcode scanning & real-time media capturing and more!

Novacura provides software and business solutions that enhance the operability of companies in various industries. Our focus is on providing industries such as logistics, distribution, and manufacturing with the best solutions that are affordable and will achieve a significant return on investment (ROI). Contact us today and see what we can do for your company.