Modern companies in various industries depend on warehouse management; therefore, this part of the business should be monitored for performance to eliminate potential inventory problems even before they occur. The best practice to avoid inventory issues is to digitize internal processes with the software capabilities of a barcode scanning system for a warehouse.
It is crucial to know that the software that manages the barcode system controls the complete data flow process and is responsible for the success or failure of current operations. While maintaining the best practices for barcode warehouse management system implementation, it is crucial to understand the technology behind the solution. A well-functioning WMS software can fully support the barcode implementation in the warehouse, allow for the reduction of inventory discrepancies and data backlogs resulting from insufficient data management, and enable high accuracy in ongoing business operations.
Warehouse barcode system and its technology
What is a barcode?
Barcodes are visual representations of data, typically a sequence of numbers and/or characters, encoded into a pattern of lines, spaces, or squares. The data in barcodes is based on references containing descriptive information. Barcodes do not have any item details; it is just a number that allows data retrieval from or transmission to an ERP system or a similar database. Reading barcodes is only a data entry method, but it is nevertheless a very efficient system compared to paper-based and repetitive manual registration in an ERP system.
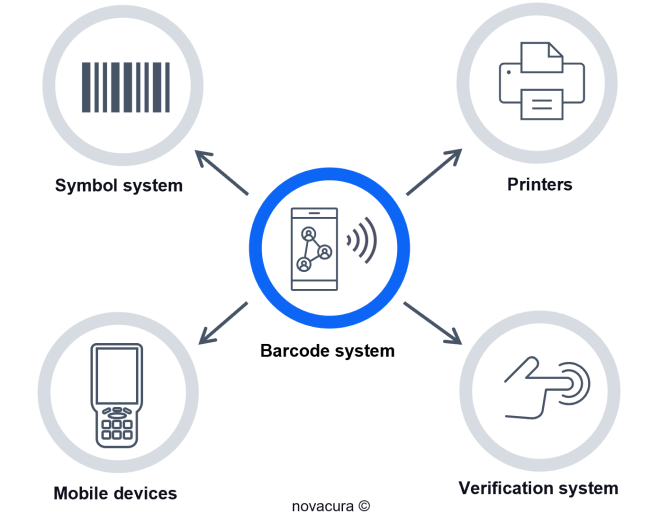
Barcode technology consists of four elements that allow the classification of objects in a warehouse:
-
Symbol System: Optical codification of an object’s reference number, commonly known as a barcode or QR code, which consists of coded information based on Code 39, Code 128, Interleaved 2 of 5 (used by airlines), UPC (Uniform Product Code), EAN (European Article Numbering).
-
Printers: Label devices with readable symbols dedicated to mobile devices’ RFID or image reading capabilities.
-
Mobile Devices: Scanners, tablets, cell phones, or other decoders with the capability of capturing images of symbols and converting them into digital information transmitted to ERP via WMS software.
-
Verification and Validation System: A system that assists in recognizing the compliance of each barcode for an asset, helping maintain the quality of the information system.
Warehouse scanning systems – the barcode descriptive information
Vertical lines shape the barcode image with spaces; in the case of QR codes, it is a composition of quadrants enclosed in a square image. After the barcode data is scanned and loaded into the mobile device, the descriptive information is transmitted to the WMS by radio frequency. The symbols are decoded and converted into typed characters that can be further transmitted to the ERP system.
Barcode images can carry and pull ERP data to scanners with descriptive information as it follows:
- LOT, SKU, part number: base information about the object on the location.
- Quantity (QTY): the required number of items stored on the location.
- Supplier identification (ID): information about the origin of the object.
- Serial Number (SN): contains more detailed data distinguishing items in the return cycle.
- Expiry date: contains data defining the product’s life and the inventory’s aging.
- Production data: contains the exact details regarding manufactured products from the shop floor, etc.
An example of barcode and QR code scanning from Create Handling Unit Novacura mobile app.
Warehouse barcode system – barcode scanners
Radiofrequency communication equipment (RFCE) enables routine warehouse transactions to be electronically processed, with all data decoded and transmitted to the ERP system. These inventory operations are managed by the Warehouse Management System (WMS) software using mobile devices such as barcode scanners, tablets, cell phones, etc.
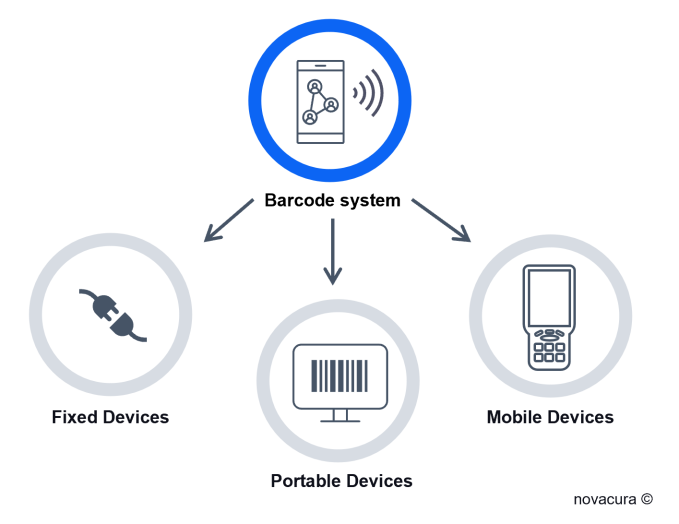
Several different devices can be used in the warehouse for barcode scanning:
-
Fixed Devices: Permanently attached to the workstation.
-
Portable Devices: Scanners capable of reading data from a barcode and storing it in internal memory until the data is transferred to the ERP system.
-
Mobile Devices: Radio frequency (RF)-based devices that can continuously communicate with the ERP system, sending updates and receiving tasks in real-time.
Both portable and mobile devices operate with rechargeable batteries. Modern WMS software primarily relies on radio frequency and mobile devices, facilitating continuous data exchange with the ERP system.
Barcode inventory system warehouse from Novacura
A barcode system holds pivotal importance in the implementation of WMS software in a warehouse. It is essential for the WMS to incorporate mobile functions, enabling employees to execute tasks remotely within the warehouse.
Novacura offers software based on the Novacura Flow low-code platform. Within the Novacura Flow solution, users have the capability to enhance the functionalities of the ERP system with WMS software.
Utilizing the Novacura Flow low-code platform, companies can create mobile and desktop applications linked to the ERP system, featuring unlimited functionalities and integrating new transactions seamlessly into the software layer over the ERP system. The use of this platform does not necessitate internal staff to possess high programming skills, and any BPM solution can be implemented on the fly.
The example presented above explains how users can use Novacura Flow, with access to Novacura Flow Studio, environment for developing applications for internal operational needs in warehouses.
Benefits of Novacura Flow
Here are the main available features and advantages that support a barcode system in a warehouse, based on Novacura Flow’s WMS solution:
-
QR and Barcode Readers: Mobile applications dedicated to tablets, handheld scanners, etc., equipped with built-in symbol readers featuring encoder and verifier functionality, which seamlessly integrate with Warehouse Management System barcode solutions.
-
On-the-Fly Changes: The use of the low-code platform allows real-time modifications to applications. This capability enables users to add additional functionality, such as barcode scanning, to mobile applications whenever needed.
-
Flexibility: Any application can be deployed with barcode scanning functionality in its interface to support various warehouse operations, such as order picking, and enterprise administrative tasks, such as registering expenses against barcode receipts or invoices.
-
Deep ERP Integration: Novacura Flow apps seamlessly integrate with ERP systems, facilitating the automatic exchange of data from Novacura mobile apps in a central database. Additionally, Novacura WMS software integrates with all printer and label systems, ensuring that the provided solution meets all barcode operations and scanning requirements.
-
Low-Cost: Building applications does not require external consultants and allows the primary system to be maintained as an ERP without costly modifications. In-house personnel can build barcode-based applications without the need for high programming skills.
SUMMARY
The barcode system plays a crucial role in warehouse operations and is essential for the smooth functioning of the company. Consequently, a WMS should incorporate this functionality as an absolute foundation. Novacura provides a Warehouse Management System (WMS) solution built on an ERP system with flexible barcode scanning functionality.
Customer case
Learn more about WMS implementation from Novacura in an US food industry, at Land O'Frost company.

Novacura offers solutions with Warehouse Management System (WMS) functionality tailored for various industries. Our software provides comprehensive support for barcode scanning functionality and diverse system integrations, ensuring users achieve optimal business results and enhance operational capabilities at a relatively low cost. By utilizing our solutions, a company can estimate Return on Investment (ROI) based on the hours spent on operational modifications. Contact us today to explore how you can enhance your operations with barcode scanning functionality from Novacura.









